How to create an External Feature Group#
Introduction#
In this guide you will learn how to create and register an external feature group with Hopsworks. This guide covers creating an external feature group using the HSFS APIs as well as the user interface.
Prerequisites#
Before you begin this guide we suggest you read the External Feature Group concept page to understand what a feature group is and how it fits in the ML pipeline.
Create using the HSFS APIs#
Retrieve the Data Source#
To create an external feature group using the HSFS APIs you need to provide an existing data source.
connector = feature_store.get_storage_connector("data_source_name")
Create an External Feature Group#
The first step is to instantiate the metadata through the create_external_feature_group method. Once you have defined the metadata, you can persist the metadata and create the feature group in Hopsworks by calling fg.save().
SQL based external feature group#
query = """
SELECT TO_NUMERIC(ss_store_sk) AS ss_store_sk
, AVG(ss_net_profit) AS avg_ss_net_profit
, SUM(ss_net_profit) AS total_ss_net_profit
, AVG(ss_list_price) AS avg_ss_list_price
, AVG(ss_coupon_amt) AS avg_ss_coupon_amt
, sale_date
, ss_store_sk
FROM STORE_SALES
GROUP BY ss_store_sk, sales_date
"""
fg = feature_store.create_external_feature_group(name="sales",
version=1,
description="Physical shop sales features",
query=query,
storage_connector=connector,
primary_key=['ss_store_sk'],
event_time='sale_date'
)
fg.save()
Data Lake based external feature group#
fg = feature_store.create_external_feature_group(name="sales",
version=1,
description="Physical shop sales features",
data_format="parquet",
storage_connector=connector,
primary_key=['ss_store_sk'],
event_time='sale_date'
)
fg.save()
The full method documentation is available here. name is a mandatory parameter of the create_external_feature_group and represents the name of the feature group.
The version number is optional, if you don't specify the version number the APIs will create a new version by default with a version number equals to the highest existing version number plus one.
If the data source is defined for a data warehouse (e.g. JDBC, Snowflake, Redshift) you need to provide a SQL statement that will be executed to compute the features. If the data source is defined for a data lake, the location of the data as well as the format need to be provided.
Additionally we specify which columns of the DataFrame will be used as primary key, and event time. Composite primary keys are also supported.
Register the metadata#
In the snippet above it's important that the created metadata object gets registered in Hopsworks. To do so, you should invoke the save method:
fg.save()
Enable online storage#
You can enable online storage for external feature groups, however, the sync from the external storage to Hopsworks online storage is not automatic and needs to be setup manually. For an external feature group to be available online, during the creation of the feature group, the online_enabled option needs to be set to True.
external_fg = fs.create_external_feature_group(
name="sales",
version=1,
description="Physical shop sales features",
query=query,
storage_connector=connector,
primary_key=['ss_store_sk'],
event_time='sale_date',
online_enabled=True)
external_fg.save()
# read from external storage and filter data to sync to online
df = external_fg.read().filter(external_fg.customer_status == "active")
# insert to online storage
external_fg.insert(df)
The insert() method takes a DataFrame as parameter and writes it only to the online feature store. Users can select which subset of the feature group data they want to make available on the online feature store by using the query APIs.
Limitations#
Hopsworks Feature Store does not support time-travel queries on external feature groups.
Additionally, support for .read() and .show() methods when using by the Python engine is limited to external feature groups defined on BigQuery and Snowflake and only when using the Feature Query Service. Nevertheless, external feature groups defined top of any data source can be used to create a training dataset from a Python environment invoking one of the following methods: create_training_data, create_train_test_split or the create_train_validation_test_split
API Reference#
Create using the UI#
You can also create a new feature group through the UI. For this, navigate to the Data Source section and make sure you have you have available Data Source for the desired platform or create new.
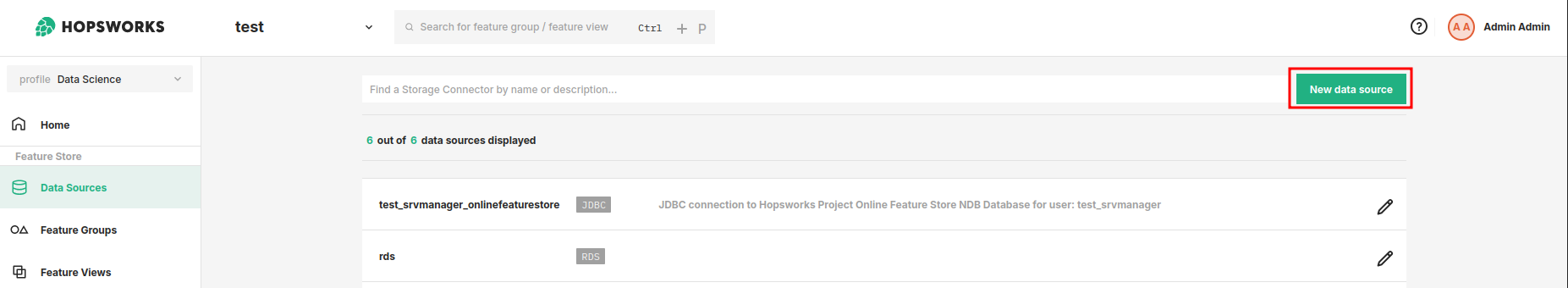
To create a feature group, proceed by clicking Next: Select Tables once all of the necessary details have been provided.
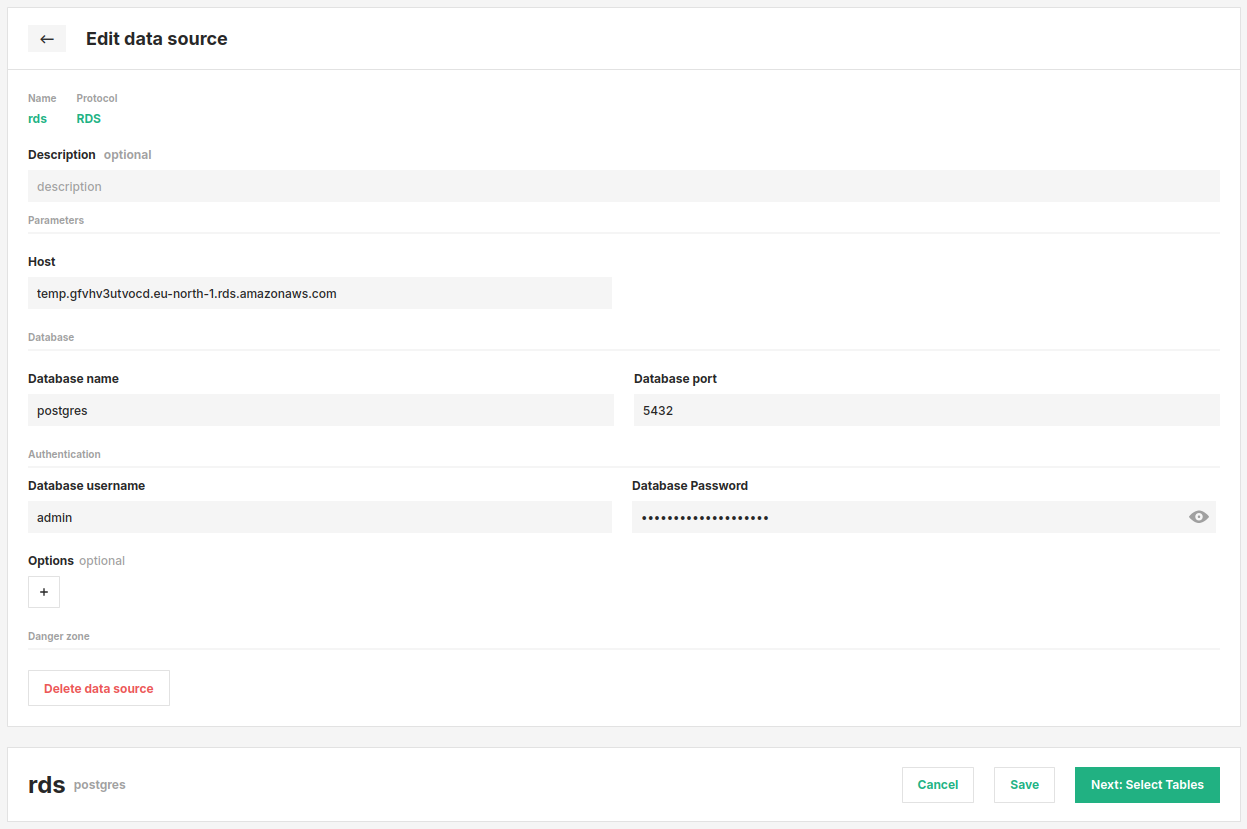
The database navigation structure depends on your specific data source. You'll navigate through the appropriate hierarchy for your platform—such as Database → Schema → Table for Snowflake, or Project → Dataset → Table for BigQuery.
In the UI you can select one or more tables, for each selected table, you must designate one or more columns as primary keys before proceeding. You can also optionally select a single column as a timestamp for the row (supported types are timestamp, date and bigint), edit names and data types of individual columns you want to include.
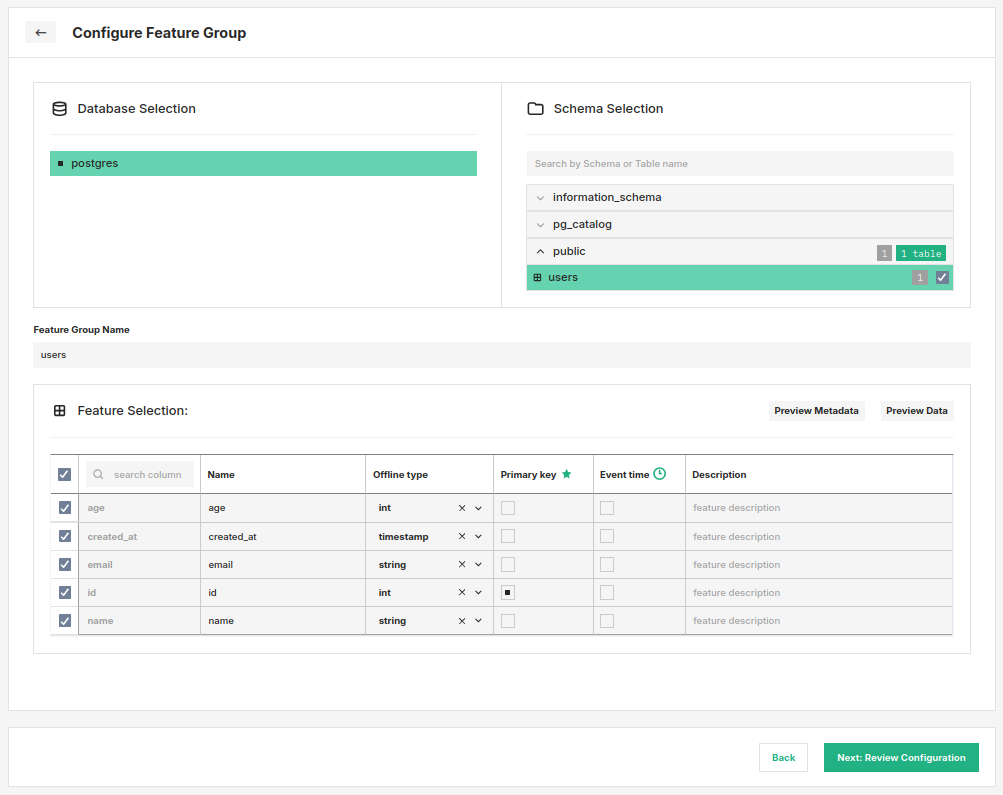
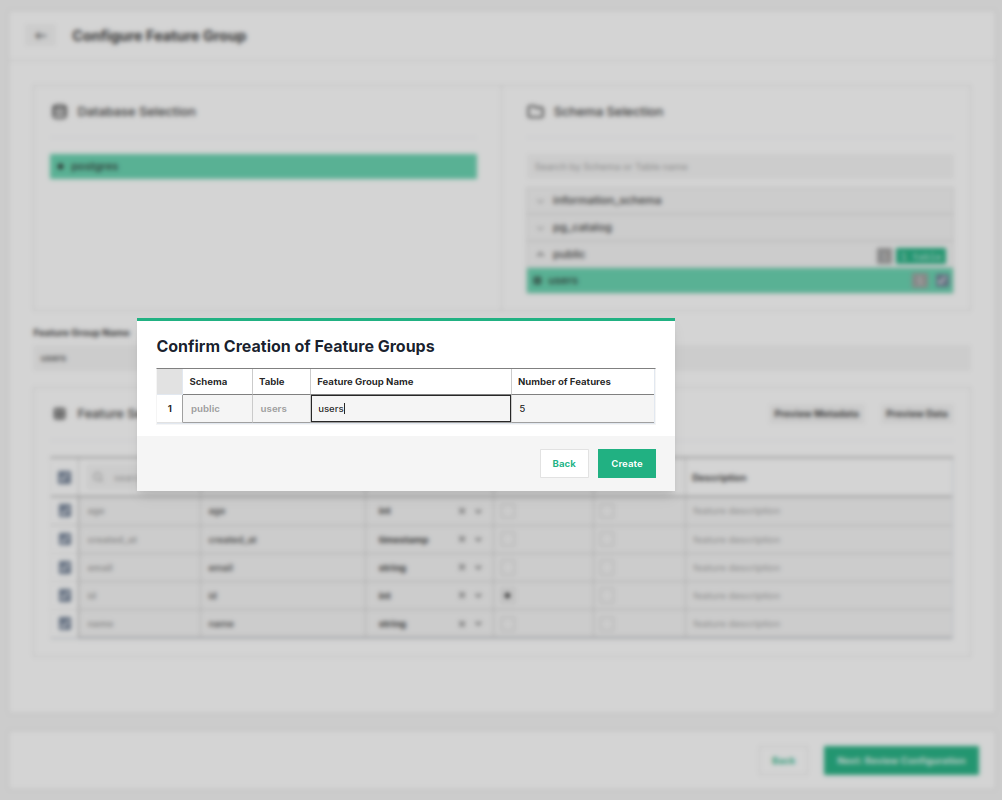
Complete the creation by clicking Next: Review Configuration at the bottom of the page. As the last step, you will be able to rename the feature groups and confirm their creation.