Adding extra configuration with generic bash commands#
Introduction#
Hopsworks comes with several prepackaged Python environments that contain libraries for data engineering, machine learning, and more general data science use-cases. Hopsworks also offers the ability to install additional packages from various sources, such as using the pip or conda package managers and public or private git repository.
Some Python libraries require the installation of some OS-Level libraries. In some cases, you may need to add more complex configuration to your environment. This demands writing your own commands and executing them on top of the existing environment.
In this guide, you will learn how to run custom bash commands that can be used to add more complex configuration to your environment e.g., installing OS-Level packages or configuring an oracle database.
Prerequisites#
In order to install a custom dependency one of the base environments must first be cloned, follow this guide for that.
Running bash commands#
In this section, we will see how you can run custom bash commands in Hopsworks to configure your Python environment.
In Hopsworks, we maintain a docker image built on top of Ubuntu Linux distribution. You can run generic bash commands on top of the project environment from the UI or REST API.
Setting up the bash script and artifacts from the UI#
To use the UI, navigate to the Python environment in the Project settings. In the Python environment page, navigate to custom commands. From the UI, you can write the bash commands in the textbox provided. These bash commands will be uploaded and executed when building your new environment. You can include build artifacts e.g., binaries that you would like to execute or include when building the environment. See Figure 1.
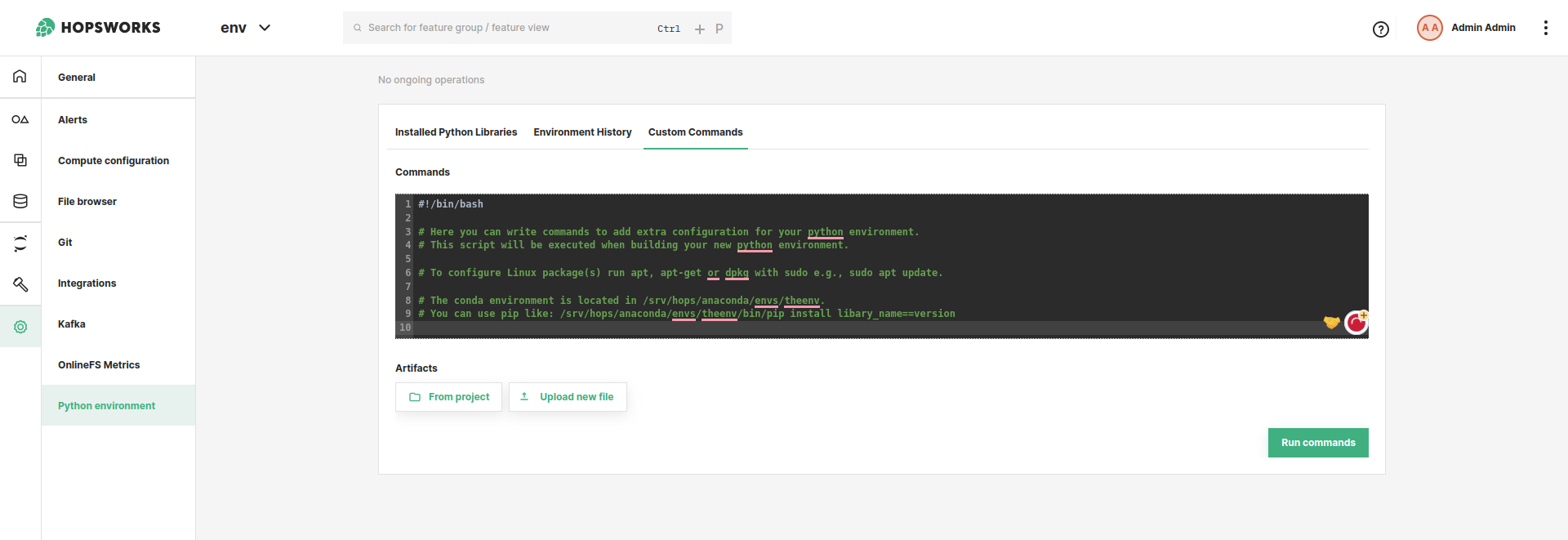
Code#
You can also run the custom commands using the REST API. From the REST API, you should provide the path, in HOPSFS, to the bash script and the artifacts(comma separated string of paths in HopsFs). The REST API endpoint for running custom commands is: hopsworks-api/api/project/<projectId>/python/environments/<environmentName>/commands/custom and the body should look like this:
{
"commandsFile": "<pathToYourBashScriptInHopsFS>",
"artifacts": "<commaSeparatedListOfPathsToArtifactsInHopsFS>"
}
What to include in the bash script#
There are few important things to be aware of when writing the bash script:
- The first line of your bash script should always be
#!/bin/bash(known as shebang) so that the script can be interpreted and executed using the Bash shell. - You can use
apt,apt-getanddebcommands to install packages. You should always run these commands withsudo. In some cases, these commands will ask for user input, therefore you should provide the input of what the command expects, e.g.,sudo apt -y install, otherwise the build will fail. We have already configuredapt-getto be non-interactive - The build artifacts will be copied to
srv/hops/build. You can use them in your script via this path. This path is also available via the environmental variableBUILD_PATH. If you want to use many artifacts it is advisable to create a zip file and upload it to HopsFS in one of your project datasets. You can then include the zip file as one of the artifacts. - The conda environment is located in
/srv/hops/anaconda/envs/hopsworks_environment. You can install or uninstall packages in the conda environment using pip like:/srv/hops/anaconda/envs/hopsworks_environment/bin/pip install spotify==0.10.2. If the command requires some input, write the command together with the expected input otherwise the build will fail.