Redshift
Amazon Redshift is a popular managed data warehouse on AWS.
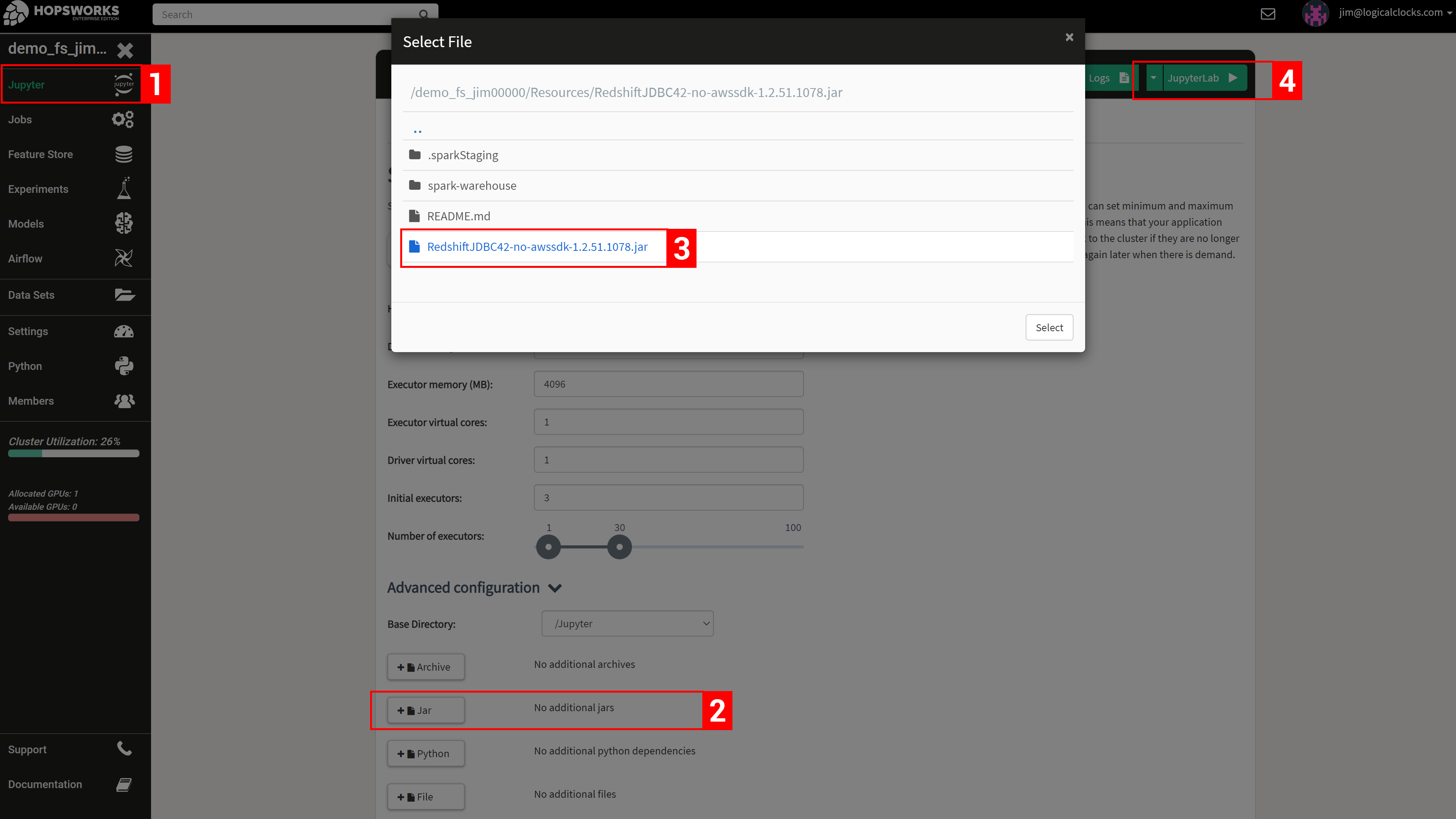
In the UI for the Redshift connector, you should enter the following:
- Cluster identifier: The name of the cluster
- Database driver: You can use the default JDBC Redshift Driver
com.amazon.redshift.jdbc42.Driver(More on this later) - Database endpoint: The endpoint for the database. Should be in the format of
[UUID].eu-west-1.redshift.amazonaws.com - Database name: The name of the database to query
- Database port: The port of the cluster. Defaults to 5349
There are two options available for authenticating with the Redshift cluster. The first option is to configure a username and a password. The second option is to configure an IAM role. With IAM roles, Jobs or notebooks launched on Hopsworks do not need to explicitly authenticate with Redshift, as the HSFS library will transparently use the IAM role to acquire a temporary credential to authenticate the specified user.
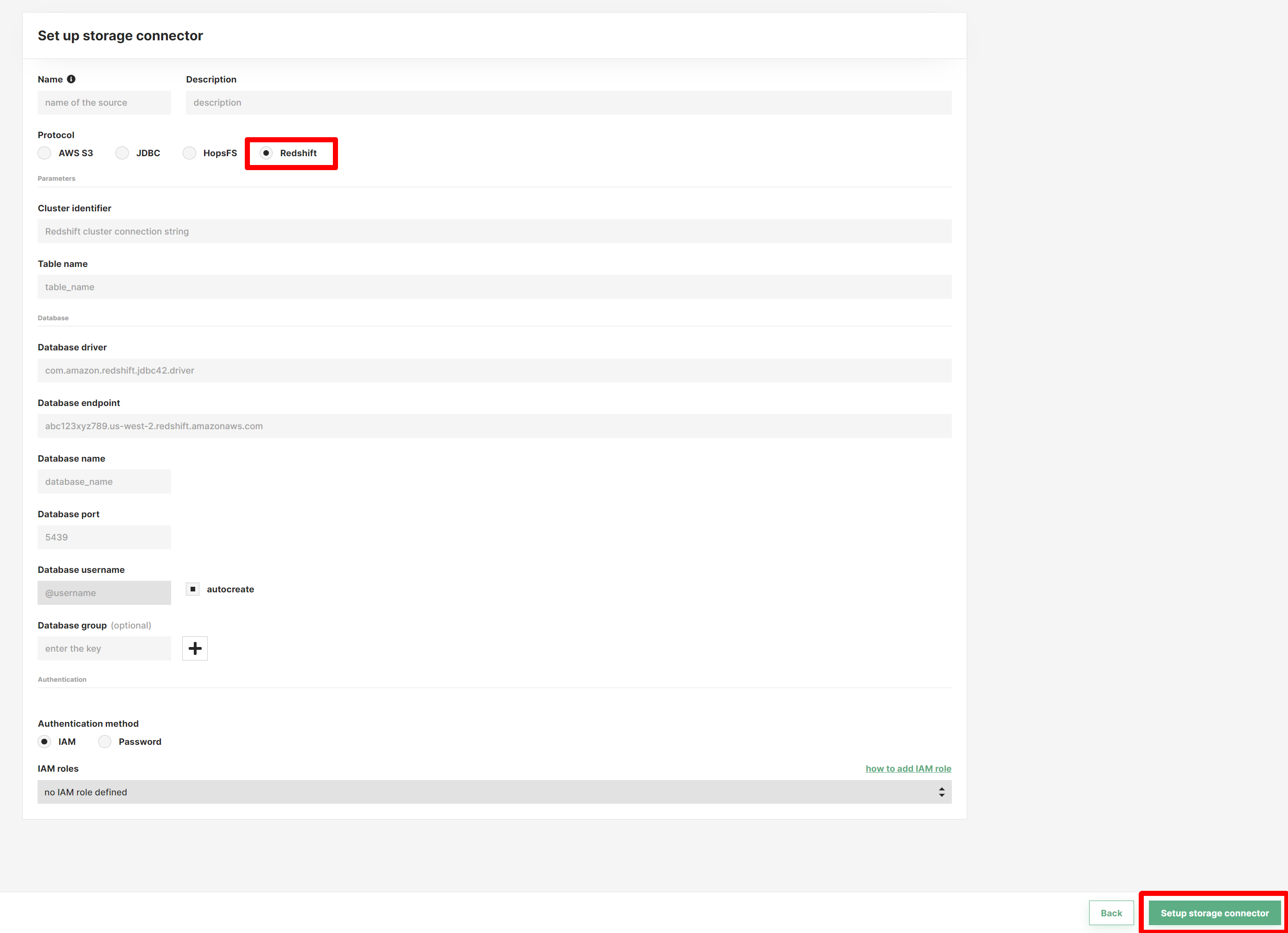
With regards to the database driver, the library to interact with Redshift is not included in Hopsworks - you need to upload the driver yourself. First, you need to download the library. Select the driver version without the AWS SDK. You then upload the driver files to the “Resources” dataset in your project, see the screenshot below.
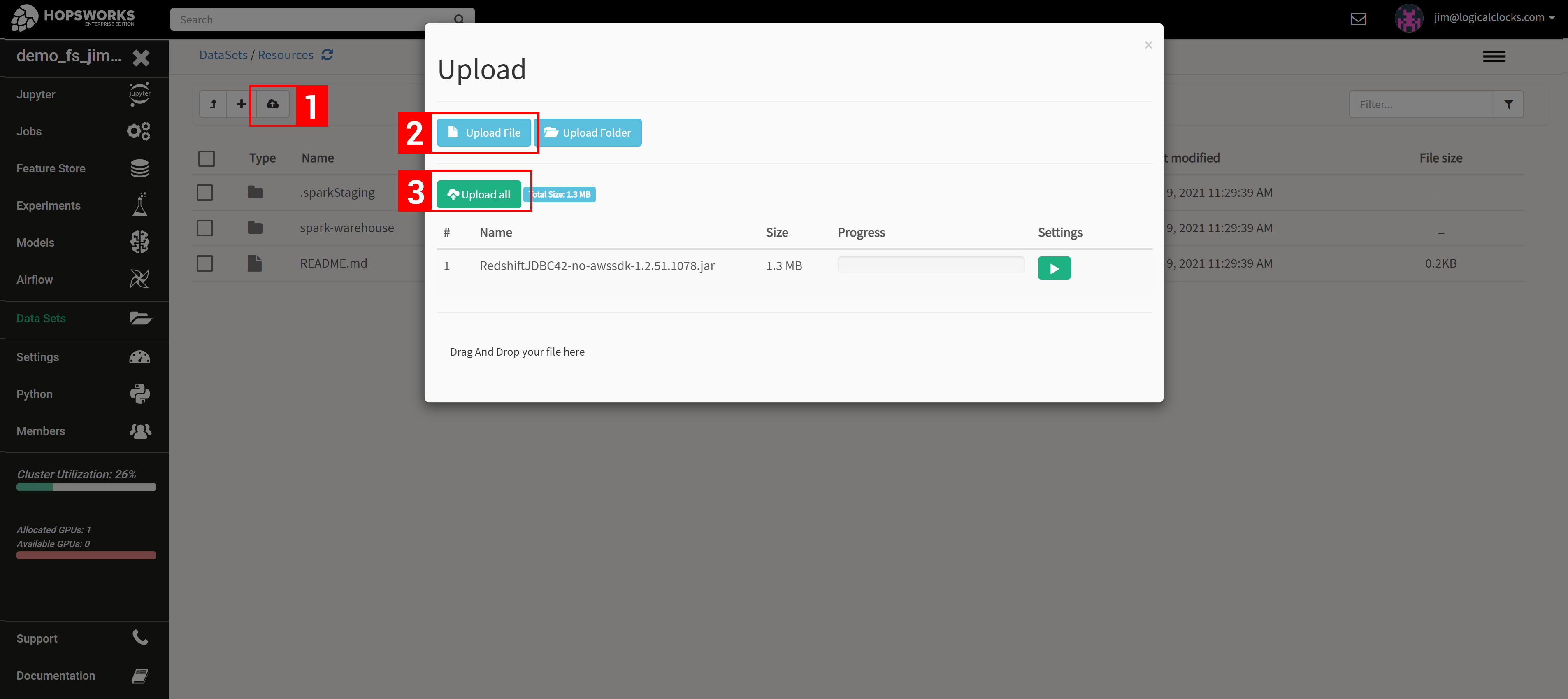
Then, you add the file to your notebook or job before launching it, as shown in the screenshots below.